CogniAgent is built around Event-Driven Automations (EDA).
EDA is an approach where systems automatically react to real-time events – such as a server alert, code commit, or user action – by triggering predefined actions. This removes manual steps from processes like incident handling, provisioning, or workflow updates and makes systems more responsive, scalable, and efficient.
How Workflows Start in CogniAgent
Every AI agent workflow in CogniAgent begins with an event.
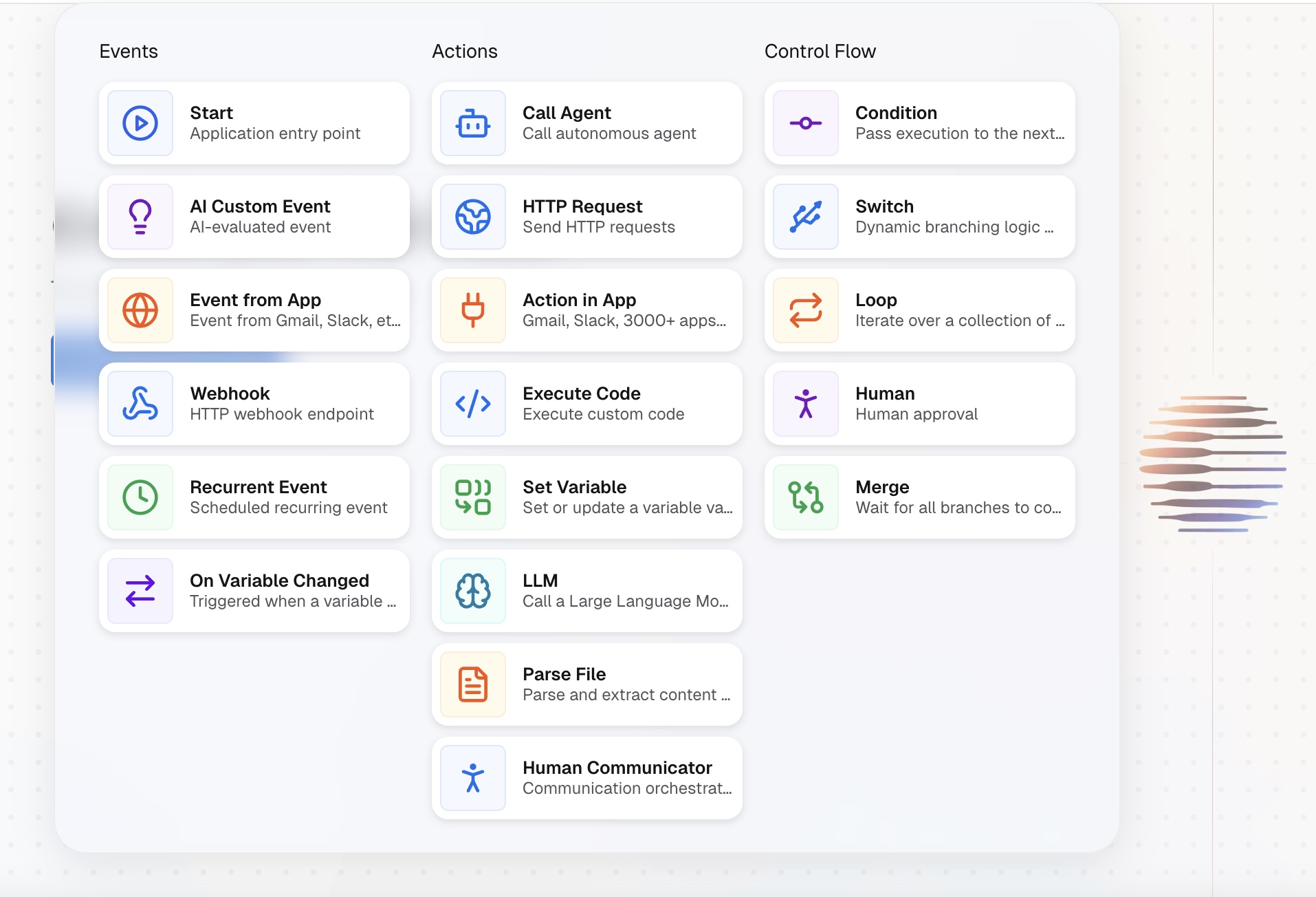
CogniAgent provides seven types of events you can use to start building workflows. Each event defines when the automation should begin.
Below is a short overview of each starting event and when to use it.
Start Event
The Start event is a manual trigger.
The workflow begins only when you explicitly click the Start button.
You may want to use this event when:
- Testing workflow behavior
- Deploying or validating new features
- Running one-time data migrations
- Requiring human oversight before execution

Recurring Start Event
The Recurring Start event triggers a workflow on a defined schedule.
For example:
- Every day at 12:00 AM
- Every Friday at 18:00
This event is best suited for:
- Generating and sending regular reports
- Periodic system checks
- Monitoring updates or competitor activity on a known cadence

Event from an App
The Event from an App starts a workflow when something happens inside a connected external service.
CogniAgent supports multiple third-party applications. You can use this event when:
- Someone posts on LinkedIn
- A partnership request or customer claim arrives in Gmail
- A supported external app triggers a predefined event
This is a pre-built, service-specific trigger. You simply connect the account, choose the platform, and the workflow listens for events such as:
- “New lead in a CRM”
- “Payment succeeded / failed”, etc.

Webhook Event
The Webhook event is used when the required external service is not available as an “Event from an App”.
A webhook allows one application to send real-time data to another when a specific event occurs, using an HTTP request instead of constant polling.
CogniAgent provides a unique Webhook URL, which you paste into the external service. When that service sends data to the URL, the workflow starts.
You may want to use this event to:
- Build custom integrations
- Connect unsupported third-party services
- Receive real-time data from external systems

AI Custom Event
The AI Custom Event is a natural-language trigger.
Instead of defining strict rules, you describe the starting condition in plain English. For example:
- “When a new invoice exceeds $500”
You then specify where AI should monitor this data, such as:
- Database updates
- Incoming emails, etc.
AI continuously evaluates the condition and triggers the workflow when it’s met.
This event is useful for:
- Sentiment-based triggers
- Complex thresholds
- Anomaly detection
Event on Variable Change
The Event on Variable Change monitors a specific data point and triggers the workflow when that value changes according to your rules.
Examples include:
- A status changing from “pending” to “completed”
- A numeric value increasing by a defined percentage
This node tracks variables across workflow execution or history. When the change occurs, AI evaluates it and proceeds based on the given instructions.
What’s Next?
Now that you know how workflows start in CogniAgent, the next step is learning how to connect these events to actions.
This is where workflows turn into executable automations and AI agents begin doing real work.
👉 Read next: Introduction to Action Nodes




