
The boardroom slides all look the same: “AI-powered,” “machine learning-driven,” “next-generation automation.” Meanwhile, engineering teams scramble to duct-tape another chatbot into production, one that can’t distinguish between a refund request and a password reset. This is something that enterprises have to handle today: an arms race where most weapons misfire. Companies pour millions into language models that generate poetic responses but can’t execute a basic order cancellation. They deploy “intelligent” agents that still require human handlers to avoid disastrous mistakes. The promised revolution feels more like expensive trial-and-error, all the while, tech leaders feel the pressure to implement AI or get left behind.
The actual game-changer? LLM agents (when implemented correctly).
There are different types of LLM agents, but in general, these tools can handle complex tasks and go beyond simple customer service:
- They can interpret ambiguous customer requests (like a human agent would)
- They can make judgment calls between policy and practicality
- And they can self-correct or add relevant information when they get something wrong
We’ve moved past the point where simply having an AI checkbox mattered. Now the question is: Does yours work?
The market doesn’t make this easy. Some vendors offer one-size-fits-all solutions that crumble under industry-specific demands. Teams waste months training models on irrelevant data. And no one feels comfortable enough to admit their shiny new agent still needs 24/7 supervision.
We created this guide to help you select LLM applications (without having a PhD in machine learning). Let’s take a closer look at different tools that perform specific tasks and handle complex problems with minimal human intervention. Explore how LLM AI agents work, discover industry-specific use cases, and assess important details before making a decision.
What Are LLM Agents?
Let’s cut through the jargon.
An LLM agent is like hiring an ultra-efficient employee who never sleeps, learns on the job, and can handle a thousand tasks at once, but instead of a person, it’s powered by AI.
Here’s a simpler breakdown:
- The brain (LLM)
- At its core, it uses a large language model (LLM) – the same tech behind tools like ChatGPT
- This gives it the ability to understand questions, analyze data, and write responses in natural language
- The difference: It does more than just talk – It acts
- A regular chatbot answers questions. LLM agents solve problems
- Example: If a customer says, “My shipment is late,” a basic bot might reply with a generic “Sorry, delays happen.” Without human intervention, LLM agents check the tracking number, identify the holdup, and offer a discount or expedited shipping
- It learns your business
- Unlike rigid, pre-programmed software, LLM agents adapt to external environments and improve over time
- The more they’re used (e.g., handling customer complaints, processing invoices), the better they get at predicting what to do next
- Where they excel
- Customer Service: Resolves 80% of routine issues instantly (refunds, returns, tech support, and various tasks)
- Operations: Monitors inventory/supply chains and flags risks before they become crises
- Data Crunching: Does data retrieval from contracts, reports, or emails to surface what matters
How do LLM Agents Work? Let’s Get Technical
At their core, LLM (Large Language Model) agents go far beyond simple question-and-answer systems. They combine sophisticated language understanding with sequential reasoning, memory, and tool integration to handle multi-step, context-aware tasks.
The Foundation
LLM agents are built on models trained using massive amounts of historical data—including books, articles, code repositories, and more. This training allows them to analyze language patterns and generate highly coherent, human-like responses. Unlike basic AI chatbots, LLM agents maintain a model context protocol, enabling them to remember the flow of ongoing conversations and user-specific details.
The Framework
These agents are supported by enhanced memory systems that can track both short- and long-term interactions. This means they can recall relevant data from previous conversations—such as a customer’s preferences or prior support issues—and use that memory to personalize future interactions.
For example:
-
An agent might remember that a specific client prefers phone calls over email—based on a conversation from over a year ago.
Agents are also integrated with external tools through APIs, allowing them to interact with:
- CRM systems for customer service and sales
- Data analysis dashboards for real-time reporting
- Inventory and workflow management platforms
Rather than following rigid scripts, LLM agents use prompt chaining, giving them far greater flexibility than traditional rules-based systems. This enables them to adapt dynamically to a user’s needs.
Decision-Making and Reasoning
A key component of LLM agents is their internal decision-making engine. They apply a technique known as chain-of-thought reasoning, which helps them break down complex problems step-by-step. This allows them to consider multiple scenarios, apply best practices, and even adjust their behavior based on state-specific regulations or compliance frameworks.
Every task begins with analyzing the context of the request. From there, the agent formulates a structured plan to achieve the desired outcome.
Real-World Execution Flow
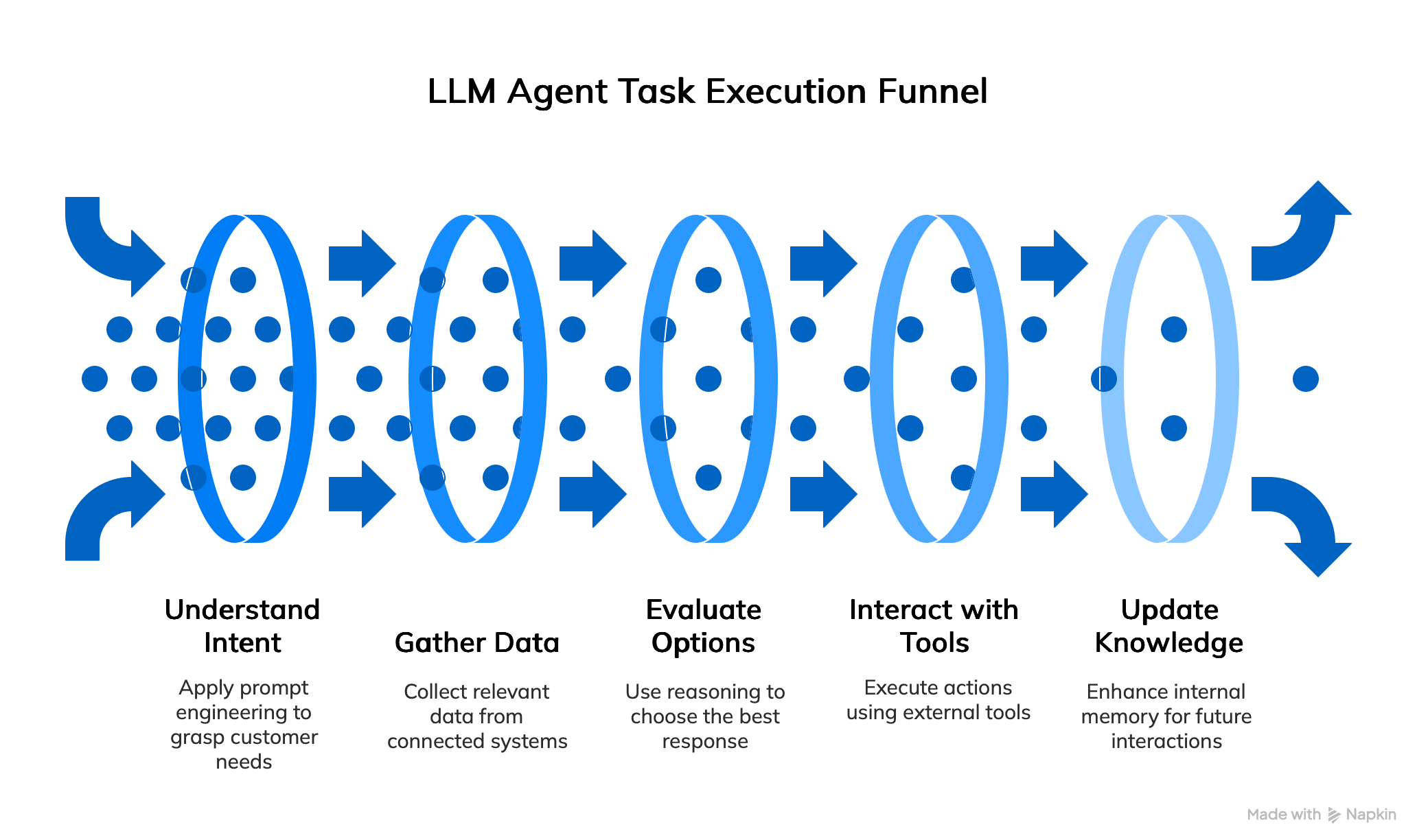
Take a customer support request, for example. Here’s how the agent typically handles it:
- First, it applies prompt engineering methods to fully understand the customer’s intent.
- Next, it pulls relevant data from connected systems (like a CRM or helpdesk).
- Then, it uses its reasoning capabilities to evaluate options and choose the most effective response path.
- It may interact with multiple external tools, placing an order, updating an account, or scheduling a service.
- Finally, it updates its internal memory and knowledge base to improve future interactions.
- This continuous feedback loop helps LLM agents learn, adapt, and perform increasingly complex tasks with accuracy and nuance.
Types of LLM Agents
LLM agents are versatile and transformative (we already know this). However, deploying the wrong type of agent can lead to costly failures, frustrated teams, and underwhelming ROI. So, let’s explore the major categories of LLM agents, how they function, and where they deliver real-world impact to help you choose the correct one:
Task-specific agents
These agents are experts. They’re narrow, but no other agent can match them in their domain. Task-specific agents are engineered for one job, and they do it flawlessly. Unlike general-purpose chatbots, these agents operate within strict parameters, combining LLM reasoning with domain-specific tools to execute precise actions.
How they work:
- Focused training: Fine-tuned on niche datasets (e.g., medical transcripts, legal contracts)
- Tool integration: Hardwired to industry software (e.g., CRM refund systems, inventory APIs)
- Deterministic outputs: Designed to minimize creative “hallucinations”
Examples:
- Customer service refund agents
- Healthcare triage bots
- Legal clause reviewers
Multi-agent systems
These types of agents collaborate like a human workforce. They divide complex workflows among specialized sub-agents, and each handles their step before passing the task forward.
How they work:
- Role Assignment: Different agents take on distinct roles (e.g., “researcher,” “validator,” “executor”)
- Orchestration Layer: A supervisor agent coordinates communication and resolves conflicts
- Parallel Processing: Multiple tasks advance simultaneously for speed
Examples:
- E-commerce complaint resolution
- Financial fraud detection
Autonomous goal-seeking agents
These agents follow instructions, but also set their own objectives.
How they work:
- Goal-Driven Loops: Continuously evaluate outcomes against KPIs (e.g., “reduce customer churn”)
- Exploration vs. Exploitation: Balances tried-and-true methods with experimental approaches
- Self-Correction: Abandons ineffective strategies autonomously
Examples:
- Programmatic ad buyer
- Autonomous supply chain agent
- Dynamic pricing engine
Conversational interface agents
These agents prioritize natural dialogue over rigid workflows. They excel in sales, therapy, or negotiation – any scenario where tone, empathy, and long-term context matter more than transactional speed.
How they work:
- Persona Customization: Adopts brand voice (e.g., “friendly tech support” vs. “formal banker”)
- Long-Term Memory: Retains user preferences across sessions
- Emotional Intelligence: Detects frustration, confusion, or urgency via sentiment analysis
Hybrid human-in-the-loop (HITL) agents
These agents blend automation with human oversight. They handle routine tasks independently but recognize their limits, and they seek human help for edge cases (e.g., legal disputes, medical emergencies).
How they work:
- Confidence Thresholds: Flags low-confidence decisions for review
- Seamless Handoffs: Provides human agents with full context (e.g., “Customer asked about GDPR—here’s the transcript”)
- Continuous Learning: Human corrections improve future autonomy
Examples:
- Insurance claim adjuster
- IT helpdesk agent
- Content moderator
These are examples of some of the major LLM agents used in various industries today. Choosing the right type for your business is about matching the agent’s architecture to the complexity of your problem. Below, we’ll explore how to select an LLM agent that fits your needs.
LLM Agents vs. Chatbots
As the AI sector develops, we’re expecting to see a market crowded with tools that promise to automate conversations. But not all are created equal. While traditional chatbots have been the go-to for basic customer interactions, LLM agents represent a fundamental leap in capability. The key difference? Chatbots follow scripts – LLM agents understand context and take action.
Chatbots operate like digital phone trees (they have limited to predefined responses). They’re not essentially bad – they’re just inefficient when handling complex conversations and tasks. They work fine for simple FAQs but break down when faced with unexpected queries. LLM agents, on the other hand, possess decision-making logic, which allows them to interpret intent, pull information, make judgment calls, and improve over time.
Here’s a better way to showcase the difference between vertical LLM agents and regular chatbots:
| Capability | LLM Agents | Traditional Chatbots |
| Understanding | Grasps nuance, slang, and intent | Limited to keyword matching |
| Adaptability | Learns from interactions and adjusts responses | Static, rule-based logic |
| Tool Integration | Connects to APIs (CRM, inventory, payment systems) | Isolated—no external actions |
| Problem-Solving | Can chain multiple steps (e.g., check order → process refund → notify team) | Handles one question at a time |
| Error Handling | Detects confusion and escalates intelligently | Fails silently or loops endlessly |
| Scalability | Improves with use (retains context across conversations) | Requires manual updates to “learn” |
| ROI | Reduces labor costs by automating complex tasks | Only replaces basic FAQs |
Chatbots have a simple purpose: to help human agents with routine tasks and answer simple customer questions. So, what are LLM agents, then? They’re a clear upgrade from simple tools to help you handle customers who expect personalized services or tackle complex operations that require real-time decisions.
How do Companies Use LLM Agents? Real-World Applications
Yes, these agents sound impressive in theory, but their real value comes from the tangible business impact. Tech leaders are already implementing these tools to automate complex workflows and can measure the value they deliver. Want to learn more about the LLM agents’ examples and their use cases? Here’s a little guide to help you understand how you can use AI agents in your company:
Hyper-personalized customer support
A global telecom company may deploy AI agents to handle at least 60% of its customer inquiries. These agents can analyze conversation history, tone, and account details in real time, which allows them to provide personalized assistance.
For example, when a customer says, “My internet is down,” the agent:
- Checks outage maps and account status
- Runs a remote diagnostic test
- Either fixes the issue or schedules a technician
Why is this revolutionary? With the help of autonomous agents, 80% of issues can be resolved without spending valuable human time, while lowering operational costs by up to 40%.
Autonomous sales negotiators
Let’s say a B2B software firm uses agents to handle contract discussions. The agent can review a client’s budget and needs, then:
- Adjust pricing tiers dynamically
- Generate custom contract terms
- Escalate only complex legal clauses to humans
The company benefits from 30% faster deal closures and 15% larger deal sizes from optimized pricing.
Supply chain autonomous agents
A retailer may use LLM agents to manage global inventory. The system predicts demand spikes using weather, trends, and events. It can also auto-order stock from the cheapest supplier and reroute shipments around delays. The use of AI agents in supply chain management has shown 50% fewer stockouts and 20% lower inventory costs for most companies.
Autonomous financial analysts
A multinational bank may use AI agents to transform its commercial lending process. The system can ingest thousands of loan applications daily and automate cross-referencing. What makes the agent so revolutionary is its ability to assess non-traditional risk factors (satellite imagery of business properties, social media for reputation signals, etc.). An application like this is especially beneficial because it doesn’t just flag risks but also structures alternative loan terms.
These examples demonstrate how the meaning of autonomous agents has evolved from simple automation to strategic partnership. The most successful deployments share three key characteristics:
- Process ownership
- Explainable decision-making
- Adaptive learning
10 Best LLM AI Agents in 2025
AI tech is evolving, and as LLM agents are becoming essential tools for businesses, we decided to create this list of the best autonomous AI agents to help you get more acquainted with their features, strengths, and ideal use cases.
#1. CogniAgent

Best For: Comprehensive business automation across departments
CogniAgent is a voice-enabled AI platform that integrates emotional intelligence and advanced conversational capabilities to manage complex workflows. It can handle any data type (PDFs, spreadsheets, APIs, etc) without requiring additional formatting or setup. With a 5-minute no-code deployment, CogniAgent combines true workflow automation with conversational intelligence, making it a disruptive force in enterprise automation.
Main Features:
- Voice-enabled with real-time emotion detection.
- Handles multi-step workflows autonomously.
- Processes unstructured and structured data without constraints.
- Instant deployment with no coding.
- Seamless integration with 2,700+ apps and platforms.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fast, no-code deployment | Voice usage may incur high costs |
| Emotion-aware voice interaction | Advanced features may need higher-tier plans |
| Supports all data types without formatting | May require configuration for specialized integrations |
Pricing: Transparent usage-based model ($0.15/minute).
#2. Devin AI
Best For: Autonomous software development workflows
Devin AI by Cognition Labs is a groundbreaking AI software engineer capable of planning, writing, testing, and debugging code with minimal input. It acts like a junior developer who takes task instructions and executes full-stack projects end-to-end—ideal for startups, dev teams, or rapid prototyping.
Main Features:
- Full-stack coding from prompt to deployment
- Real-time debugging and troubleshooting
- Interfaces with GitHub, CLI, and web tools
- Task breakdown and auto-planning
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Accelerates software delivery | Not suited for legacy stack customization |
| Handles entire dev lifecycle | Enterprise access is still limited |
| Excellent for prototyping | Not yet fully open to the public |
#3. Manus AI
Best For: Fully autonomous, general-purpose task execution
Manus is a next-gen LLM agent built for complex task planning and real-world execution. It mimics human reasoning across domains – capable of answering questions, deploying apps, conducting research, and iterating independently. Think of it as your autonomous business analyst or junior ops agent.
Main Features:
- Self-directed reasoning and execution
- Goal decomposition into actionable steps
- Multimodal support (code, text, tools)
- Plug-and-play with external APIs
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Truly autonomous multi-step actions | Still experimental in some edge tasks |
| Fast deployment on general web tasks | Not optimized for niche domains |
| Great for internal operations | Limited UI for non-technical users |
Pricing: Request access via Manus waitlist
#4.Relay.app
Best For: Automating team communication and task delegation
Relay is designed to reduce operational overhead by assigning tasks, sending reminders, and generating meeting summaries directly in Slack or your project stack. It’s perfect for busy teams looking to automate follow-ups and cross-functional handoffs.
Main Features:
- Assigns and tracks team tasks
- Slack + project tool integration
- Generates auto-summaries and notifications
- Email support and smart reminders
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Boosts internal accountability | Less useful outside team workflows |
| No-code setup | Limited to supported platforms |
| Improves async communication | Not task-planning intelligent |
Pricing: Starts at $10/month per user
#5. Gumloop
Best For: No-code business automation for small teams
Gumloop lets users build no-code agents that automate routine business workflows like sending follow-up emails, syncing data across tools, and handling lead flows. It’s especially helpful for marketing, operations, and early-stage startups.
Main Features:
- Drag-and-drop automation builder
- Pre-built agent templates (CRM, support, ops)
- Connects to 2,000+ apps (via Zapier-style integrations)
- Schedule- or event-based execution
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Extremely easy to use | Limited in-depth reasoning |
| Great starter automation tool | Not ideal for complex logic |
| Affordable and scalable | Requires external integrations |
Pricing: Free plan available; paid starts at $29/month
#6. VoiceFlow
Best For: Building conversational AI agents for voice or chat
Voiceflow is the go-to platform for creating rich voice and chat agents without writing code. Enterprises use it to design IVRs, chatbots, and voice experiences for platforms like Alexa, Google Assistant, or in-house tools.
Main Features:
- Visual interface for conversation logic
- Multimodal support (text + voice)
- Integrates with APIs and CRMs
- Testing, simulation, and analytics included
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Ideal for designers and marketers | Not an autonomous reasoning agent |
| Enterprise-grade features | Voice-only use may limit reach |
| No coding needed | Somewhat steep learning curve |
Pricing: Free tier available; Pro from $40/month
#7. Stack AI
Best For: Automated insights for marketing and product teams
Stack AI delivers agents that monitor business metrics, detect anomalies, and suggest next actions, all powered by natural language prompts. It acts as a smart business analyst plugged into your analytics stack.
Main Features:
- Natural language querying of data
- Auto-insights and dashboards
- Integration with tools like Mixpanel, Amplitude
- Agents trained on user goals
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Speeds up data interpretation | Focused mainly on digital products |
| Reduces reliance on data teams | Requires clean, structured data |
| User-friendly analytics layer | Not built for deep BI use |
Pricing: Contact for pricing (based on seat and usage)
#8. Cognizant Agent Foundry
Best For: Enterprise-scale automation across business departments
Agent Foundry enables businesses to build task-oriented AI agents that execute within secure enterprise environments. It supports process automation, knowledge work, and compliance workflows across HR, finance, and operations.
Main Features:
- Secure deployment in enterprise clouds
- Multi-agent orchestration
- Compliance-ready with audit trails
- Deep tool and system integration
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Designed for regulated industries | Requires IT onboarding |
| Supports internal tool workflows | Best suited for large orgs |
| Robust architecture for scaling | No self-serve entry point |
Pricing: Enterprise-only, custom licensing
#9. Lindy AI
Best For: Automating executive assistant tasks
Lindy creates personalized agents for knowledge workers, automating scheduling, inbox management, writing, and even compliance checks. It’s like having a full-time EA that learns your preferences.
Main Features:
- Email summarization and response drafting
- Calendar and meeting management
- Knowledge base integration
- Trains on your work style and docs
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Highly personalized experience | Only for knowledge workers |
| Strong assistant functions | Not ideal for creative or dev tasks |
| Fast onboarding with Gmail, Calendar | Context limits across org-wide tools |
Pricing: Starting at $49/month
#10. Vocode AI
Best For: Real-time, intelligent voice bots for sales and support
Vocode enables creation of AI voice agents that can hold natural conversations – ideal for outbound sales, lead qualification, appointment booking, and Tier-1 support. It handles interruptions, rephrasing, and dynamic scripts with high call realism.
Main Features:
- Real-time voice processing
- Interrupt and rephrase detection
- CRM, calendar, and webhook integration
- Logs and analytics for every call
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Great customer interaction UX | Requires good call flows and prompts |
| Impressive voice realism | Still early in high-volume scaling |
| Automates outreach and booking | Usage-based pricing can add up |
Pricing: Usage-based (~$0.10–$0.20/minute)
How to Choose an LLM Agent?
As with every business decision, selecting the proper LLM tool requires evaluation. There are dozens of platforms available on the market (each promising transformative results). It’s essential to assess them based on your specific business needs. We prepared a structured assessment guide for you to approach decision-making with preparation.
Define the use case
Before evaluating technical features, clarify what you need the agent to accomplish:
- Customer support: Handling inquiries, troubleshooting, and escalations
- Sales and marketing: Lead qualification, personalized outreach, and follow-ups
- Operations: Process automation, data analysis, and real-time decision-making
- Internal productivity: HR assistance, IT helpdesk, and knowledge management
⚡Ask: “What specific problems am I trying to solve?”
Evaluate core capabilities
- Not all LLM agents are created equal. Prioritize these critical functionalities:
A. Reasoning & adaptability
- Does it follow rigid scripts, or can it handle unexpected queries?
- Can it chain multiple steps (e.g., check inventory → process refund → notify logistics)?
B. Integration flexibility
- What systems does it connect with (CRM, ERP, databases)?
- Can it process unstructured data (emails, PDFs, voice recordings)?
C. Learning & improvement
- Does it improve over time through feedback?
- Can it be fine-tuned for industry-specific terminology?
D. Security & compliance
- Is it SOC 2, HIPAA, or GDPR compliant if needed?
- Does it provide audit logs for decision transparency?
Assess deployment & maintenance
- Setup time: Some agents deploy in minutes; others require weeks of configuration.
- Technical resources needed: Will your IT team manage it, or is it no-code friendly?
- Ongoing costs: Look beyond licensing—consider training, API calls, and compute costs.
⚡Warning: Many platforms have hidden scaling fees.
Compare performance benchmarks
Request real-world metrics from vendors:
- Accuracy: How often does it require human intervention?
- Speed: Response times for complex queries
- ROI Examples: e.g., “Client reduced support costs by 40% in 3 months.”
⚡Tip: Ask for a proof-of-concept trial before committing.
Prioritize vendor support & roadmap
- Does the vendor offer dedicated onboarding?
- How frequently is the model updated?
- Is there a clear plan for handling regulatory changes?
⚡Red Flag: Limited documentation or slow response times during evaluation.
Choosing Your AI Agent Based on Your Industry?
| Industry | Must-Have Features | Nice-to-Have Features |
| Healthcare | – HIPAA/GDPR compliance – Symptom triage accuracy – EHR/EMR integration |
– Voice-based patient intake – Multilingual support – Predictive diagnostics |
| Real Estate | – Property database integration – Lead qualification – Contract templating |
– Virtual tour coordination – Neighborhood analytics – Mortgage calculator |
| Fintech | – Fraud detection – Regulatory compliance (SOX, PCI) – Real-time transaction monitoring |
– Personalized financial advice – Voice-enabled banking – Risk prediction |
| Telecom | – Network outage resolution – Billing/payment support – CRM integration |
– Proactive service alerts – Cross-sell/upsell automation – IoT device support |
| Travel & Hospitality | – Booking/rescheduling – Multilingual support – Dynamic pricing integration |
– Personalized itinerary planning – Sentiment-based service recovery – Voice concierge |
| Retail | – Inventory lookup – Return/refund automation – Loyalty program integration |
– Visual search (image recognition) – AR try-on support – Demand forecasting |
| E-commerce | – Order tracking – Product recommendations – Payment dispute resolution |
– Voice shopping – Social commerce integration – AI-generated product descriptions |
| Manufacturing | – Supply chain monitoring – Equipment maintenance alerts – QA defect detection |
– Digital twin integration – Predictive maintenance – Sustainability analytics |
| Logistics | – Real-time shipment tracking – Route optimization – Carrier API integration |
– Autonomous freight matching – Carbon footprint tracking – Voice-enabled dispatch |
| Food & Beverage | – Order customization – Allergy/dietary restriction compliance – POS integration |
– Voice ordering – Recipe suggestions – Waste reduction analytics |
Curious How LLM Agents Could Work for Your Team? CogniAgent will Show You
Empowered teams guarantee a prosperous future and comfortable workflows. With the right agent, you can automate those tedious and routine tasks that don’t waste too much of your team’s precious time. It’s time to free up your people to focus on what truly matters: innovation, relationships, and growth.
And you know what the best part is? You don’t have to figure it out alone.
We partner with you to build solutions that fit seamlessly into your workflows whether you’re looking for easy customer support, supercharged sales, or optimized operations.
The first step is simple. Let’s talk!
Get a demo or simply contact us if you have additional questions. Our team is happy to chat.
CogniAgent FAQ
What’s the implementation process like?
For most clients, their apps are operational in under a week. We start with your specific use cases, integrate with your existing tools, and train the agent on your business processes. No coding is needed – our team handles the setup.
How does the pricing work?
We offer transparent usage-based pricing starting at $0.15 per minute of agent interaction. Don’t worry, you won’t have to deal with hidden fees or surprise charges. (And for larger deployments, we have enterprise plans with unlimited usage.)
What kind of support do you provide?
Every client gets a dedicated onboarding specialist (we take every step alongside you), 24/7 technical support for quick questions and even quicker help, regular performance reviews, and continuous training as your needs evolve.
Can the agent work with our existing software?
Of course. CogniAgent can be integrated with over 2500 business applications (including all major CRMs, ERPs, and other productivity tools).
