Over the past few months, a bunch of companies have rolled out a new wave of AI–smart agents that can handle complex tasks all on their own.
According to analysts at Grand View Research, the global AI agent market is set to skyrocket by 45% by 2030, hitting a whopping $70.5 billion. These AI solutions won’t just speed up automation but also deliver hyper-personalized customer experiences and help everyday users offload routine tasks to AI assistants.
So, what is Agent AI? How could they evolve into a superintelligence in the future? And how can businesses make the most of them? Let’s discover!
Definition of AI Agent
AI agents are smart, autonomous systems that can interact with their surroundings, make decisions, and take action – all without human help. They’re built using machine learning and natural language processing (NLP), which lets them handle everything from simple, routine tasks to more complex problem-solving and multitasking.
What makes an AI Agent different from traditional AI? They can keep getting better over time by learning on their own.
Even though the term “AI agents” sounds new, the idea has actually been around since the 1950s. Back then, machine learning pioneer Arthur Samuel created one of the first self-learning programs – an electronic checkers player.
Fast forward to the 1960s and 70s, and we got the first chatbot, Eliza, and expert systems like DENDRAL, which could mimic human expertise. But because of tech limitations, AI hit a roadblock, leading to what’s known as the “AI winter.” Things picked up again in the 80s and 90s with better machine learning techniques. One big milestone? IBM’s Deep Blue, which famously beat chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1996.
By the 2000s, AI really took off thanks to better computing power. Virtual assistants like Siri showed how useful AI could be in everyday life. The 2010s saw even bigger breakthroughs, with reinforcement learning and generative models like GPT-2 paving the way for today’s AI agents. Now, we have advanced systems like ChatGPT that can chat, solve work problems, and even make decisions, pushing AI closer to the future we once only imagined.
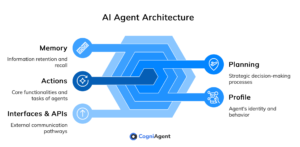
Components of AI Agents
AI agents come in different shapes and sizes. Still, they usually have five key parts:
- Interfaces & APIs – This is how agents connect with users, databases, sensors, and other systems. Think of it as their way of “talking” to the outside world.
- Memory — They have short-term memory (for keeping track of recent interactions) and long-term memory (for building up knowledge over time).
- Profile – This defines who the agent is — its role, goals, and behavior patterns. Its “personality” and purpose.
- Planning – Most agents use AI models (big or small) to map out what they need to do next.
- Actions – This part includes APIs and system connections that decide what the agent can do – sending messages, automating tasks, or pulling up info.
Put all these pieces together, and you get an AI that can think, plan, and act independently!
How AI Agents Work (In Plain English)
By connecting to different systems, AI agents use big language models to think, plan, and get stuff done. Here’s the breakdown:
- Perception – They’re constantly gathering info from their environment — user interactions, key data points, or sensor readings.
- Reasoning – Using AI models, they determine what needs to be done, prioritize tasks, and make decisions based on context, goals, and other factors.
- Action – Once they have a plan, they use built-in interfaces to interact with tools, databases, and business systems (like HR platforms, order management, or CRMs).
They can even pass tasks to other AI agents or check in with users.
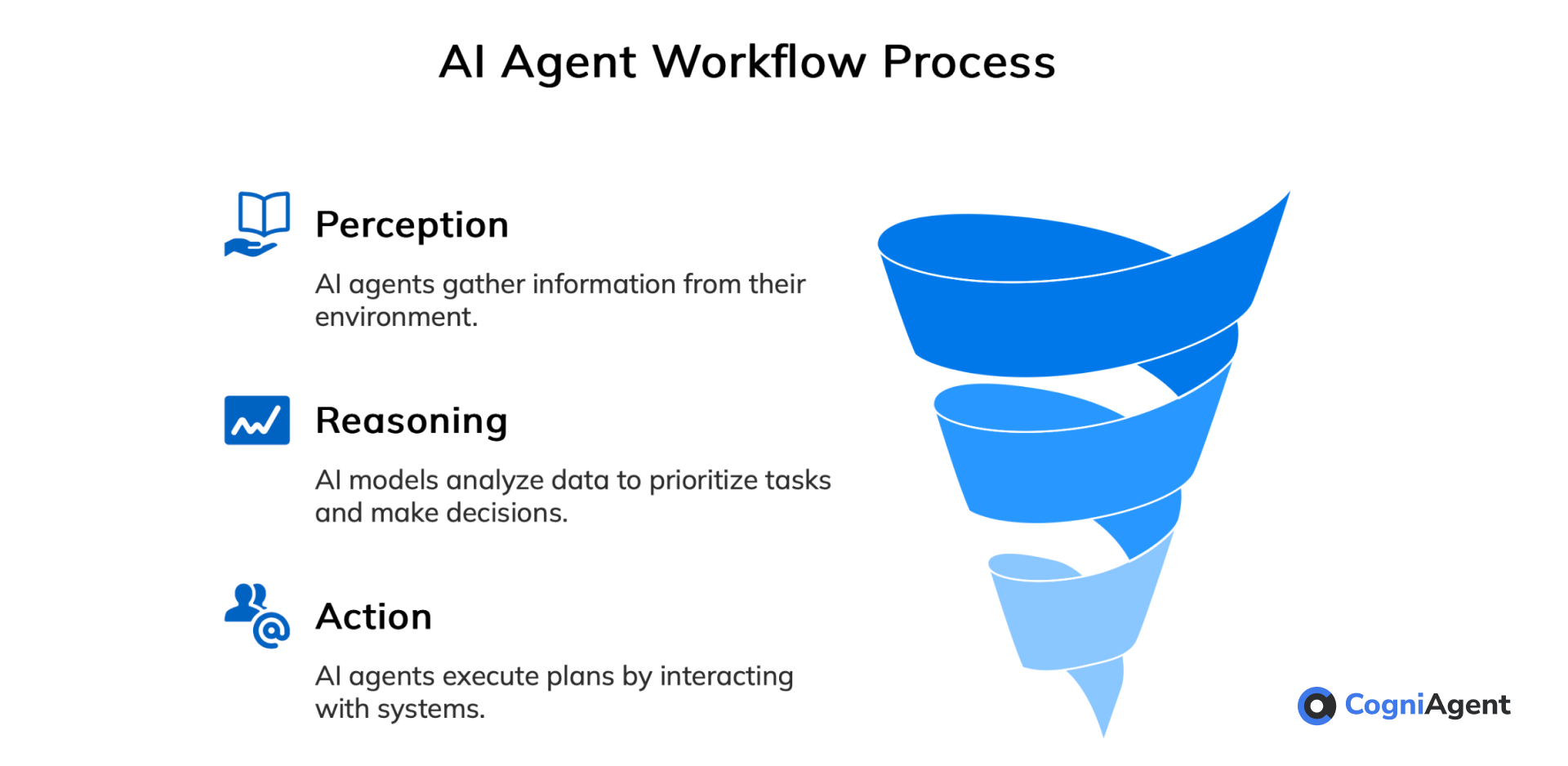
Some agents also use search-augmented generation (RAG) to pull in real-time info from external sources, like the internet, to stay up-to-date.
This whole “sense-reason-act” cycle runs on its own, meaning the agent keeps analyzing past interactions, learning, and improving over time — basically, getting more competent with every task.
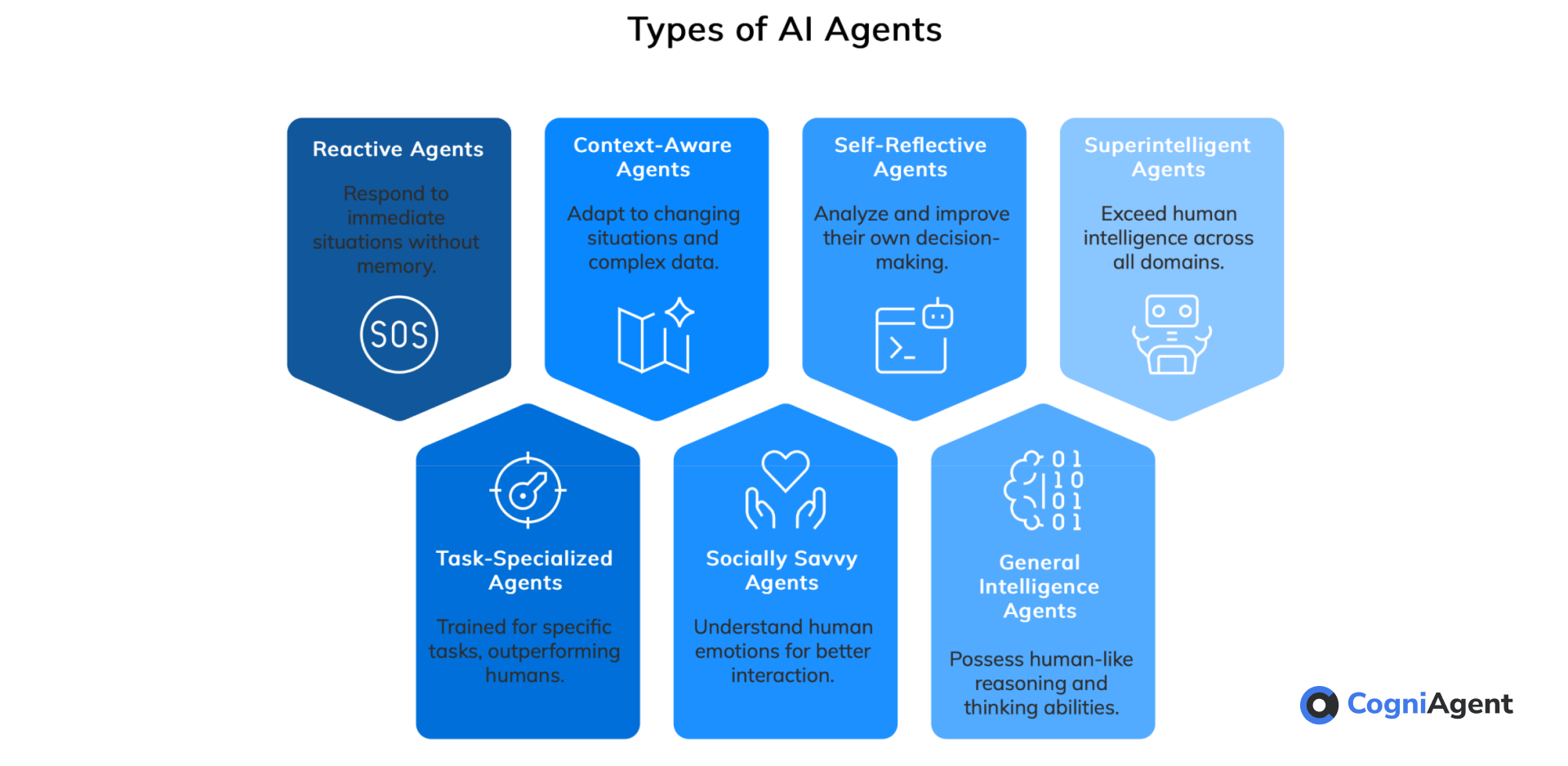
Types of AI Agents (Made Simple)
AI agents come in different levels, kind of like evolving video game characters. Depending on how advanced they are, they fall into a few categories:
- Reactive Agents – These guys only respond to what’s happening right now. No memory, no learning—just following preset rules.
- Task-Specialized Agents – They’re trained on specific tasks and can get really good at them, often better than humans (think AI doctors or chess engines).
- Context-Aware Agents – These AIs can handle changing situations and process different kinds of complex data, adapting as they go.
- Socially Savvy Agents – They pick up on human emotions, beliefs, and intentions, which makes them great for customer support or therapy bots.
- Self-Reflective Agents – These are next-level AIs that can actually analyze their own decisions and tweak their own algorithms to improve.
- General Intelligence Agents – This is full-on AGI (artificial general intelligence), meaning an AI that can think and reason like a human.
- Superintelligent Agents – The sci-fi dream (or nightmare?). These would be smarter than humans in every way, driving massive breakthroughs in science, economics, and more. Philosopher Nick Bostrom first talked about this, but we’ll probably need quantum computing to make it real.
Some experts also group AI agents by autonomy levels, from basic L1 agents to fully independent L5 agents. Right now, AI models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini are considered L1, while OpenAI’s new Operator AI agent is closer to L2 since it can make decisions on its own.
Conclusion
AI agents are transforming the way we work, automate tasks, and interact with technology. From simple reactive bots to advanced self-learning systems, these intelligent assistants are becoming more capable, helping businesses streamline operations and making AI-powered tools more accessible to everyone.
With the market expected to grow rapidly in the coming years, we’re just beginning to see what AI agents can do. As they continue to evolve, they could bring us closer to artificial general intelligence (AGI) and even more advanced systems. Whether that future excites or raises concerns, one thing is clear – AI agents are here to stay, and they’re only getting smarter.
The real question now is how businesses and individuals will embrace this AI-driven future.